Guide: What Is Stamping?
Leave a CommentAs the global markets continuously evolve, the demand to quickly produce large quantities of high-quality complex parts rises simultaneously. Because of this, stamping, a popular manufacturing process, has been sought-after by many manufacturers as a cost-effective and efficient solution to large-quantity manufacturing needs in various industries.
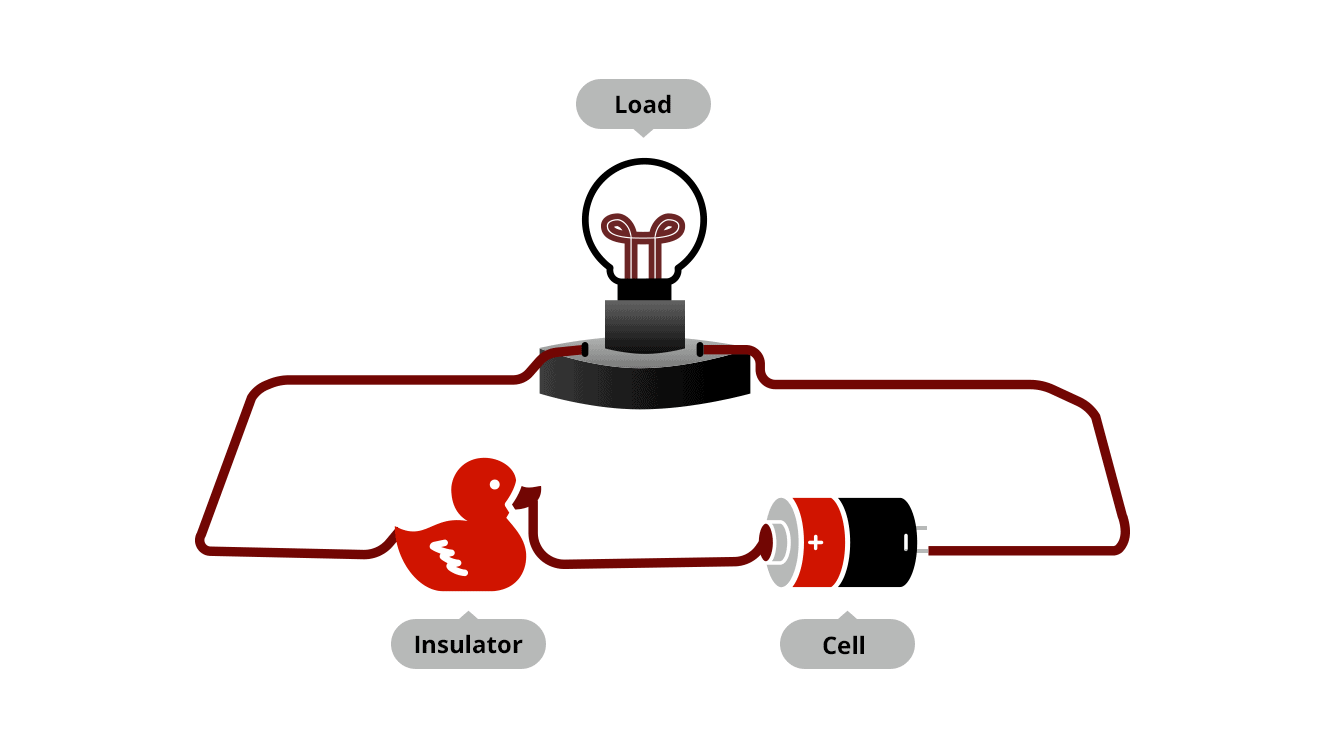
One of the popular processes in the manufacturing industry is metal stamping. However, non-metal stamping, especially stamped parts made from electrical insulation and barrier materials, is also gaining popularity among many manufacturers in fabricating different components for various purposes.
As a leading supplier of a large inventory of stamped products, ESPE Manufacturing Co. specializes in stamping electrical insulation, barrier materials, and other non-metallic materials such as plastic, rubber, paper, and more! This article will walk you through what stamping is in the manufacturing industry, its benefits, and its applications.
Stamping In Manufacturing
Also referred to as pressing, stamping is a manufacturing process of converting or altering flat sheets into different shapes to produce a valuable component or part. The process is usually carried out on sheet metal. But it can also be used on other non-metal materials, including a broad range of specialty polymers, aramid papers, neoprene, acrylic, and more.
The stamping process involves placing your material of choice in a stamping press where a tool and die surface form the workpiece into a final shape. Parts or components produced from stamping are used in automotive, electronics, medical, defense, aerospace, and many other sectors.
Non-Metal Stamping Operation
ESPE’s stamping operations involve slitting material and feeding it into the presses, where stamping takes place at 50-200 strokes per minute.
When selecting a non-metal material for a stamping operation, it is essential to consider a few factors to achieve optimal production and performance, including the material’s properties and characteristics.
Manufacturers should look at the material’s mechanical, electrical, magnetic, and thermal properties, as well as its durability and performance under normal and high-stress operating conditions. Moreover, the design for stamping should also meet the application’s absorption, compression, and alignment requirements.
Benefits Of Stamping
Manufacturers utilize the stamping technique because it is time- and cost-efficient. Specifically, stamping provides the following advantages:
Precision
Stamping reaches a micron-level accuracy on the cuts applied to the sheet material. Hence, this process’s sophistication and intricate nature allow manufacturers to shape and sell parts in the most complex forms at the highest quality.
Cost Efficiency
Stamping enables manufacturers to mass produce parts with lower labor costs, which helps to achieve lesser expenditures and higher profit.
Versatility
Detailed part specifications are easily achieved through stamping, as it allows for alteration of the shape and design of material into any desired form, even the more complex ones.
Advantages of Non-Metallic Stamping
In addition to the general benefits of stamping, there are a couple of advantages in stamping non-metallic parts and products, like electrical barriers and insulators, including:
Mass Production
The tools that shape and cut sheet materials are called stamping dies. These dies can be used for multiple production runs or swapped out quickly for different parts, making the stamping process fast and efficient.
Higher Accuracy
With durable dies set up, the stamping process can produce high volumes of identical parts with strict tolerances.
Application
The common industries that utilize stamped electrical barriers and insulators, and other non-metallic parts and components include:
- Aerospace
- Agriculture
- Architecture
- Automotive
- Dental
- Electronics
- Food and Beverage
- Machine tools
- Marine
- Medical
- Oil and gas
- Packaging
- Renewable energy
- And more
Top-Quality Stamping Services At ESPE Manufacturing Co.
ESPE Manufacturing Co. understands the fundamental role of stamping in responding to the manufacturing industry’s growing demands for different components or custom parts supply. We live up to our reputation as the technical authority in producing the best quality stamped parts.
Our stamping outputs are made from electrical insulation and barrier materials, such as ITW Formex®, ITW Statex®, and Nomex®, as well as vulcanized fiber and fishpaper. We also offer non-metal materials like polymers, vinyl, acrylic, nylon, and aramid papers. We manufacture thousands of products from stamping, such as washers, arc chutes, and other insulators — from prototype to production quantities.
ESPE Manufacturing Co. is your partner for proficient and top-quality stamping operations that involve compound die, progressive die, and punch press, which allow us to sustain and meet any geometric complexities, designs, and specifications!
Contact us directly to learn more about our stamping capabilities or request a quote today, and our friendly experts will be happy to assist you.