What to Know About Electrical Insulating Materials
Leave a Comment
At ESPE Manufacturing, we specialize in the manufacture of high-quality custom plastic parts and products, including electrical insulating materials. We maintain an extensive inventory of non-metallic materials for use in our manufacturing operations and distribution to our customers. One of our core material offerings is electrical insulation. Below, we provide an overview of this material, including what it is, why it is needed, how it is used, typical applications, and types available.
The 5 Basic Aspects of Electrical Insulation
1. What Is Electrical Insulation?
Electrical insulation refers to materials that do not allow electricity to flow through them freely (e.g., rubber or plastic). In contrast, conductors and semiconductors do allow electricity to flow through them freely (e.g., copper). This difference in performance stems from the difference in their resistivity. Electrical insulating materials have higher resistivity than semiconducting and conducting materials, which means electrons do not pass as easily through the former as they do through the latter.
2. Why Is It Needed?
Electrical insulators help control the flow of electricity. They ensure energy reaches the desired destination within the system by acting as a barrier around the conductor, preventing the energy from straying from the preferred path. In doing so, they also prevent electricity from flowing to other components, which can cause short-circuiting or electrocution depending on the configuration of the system.
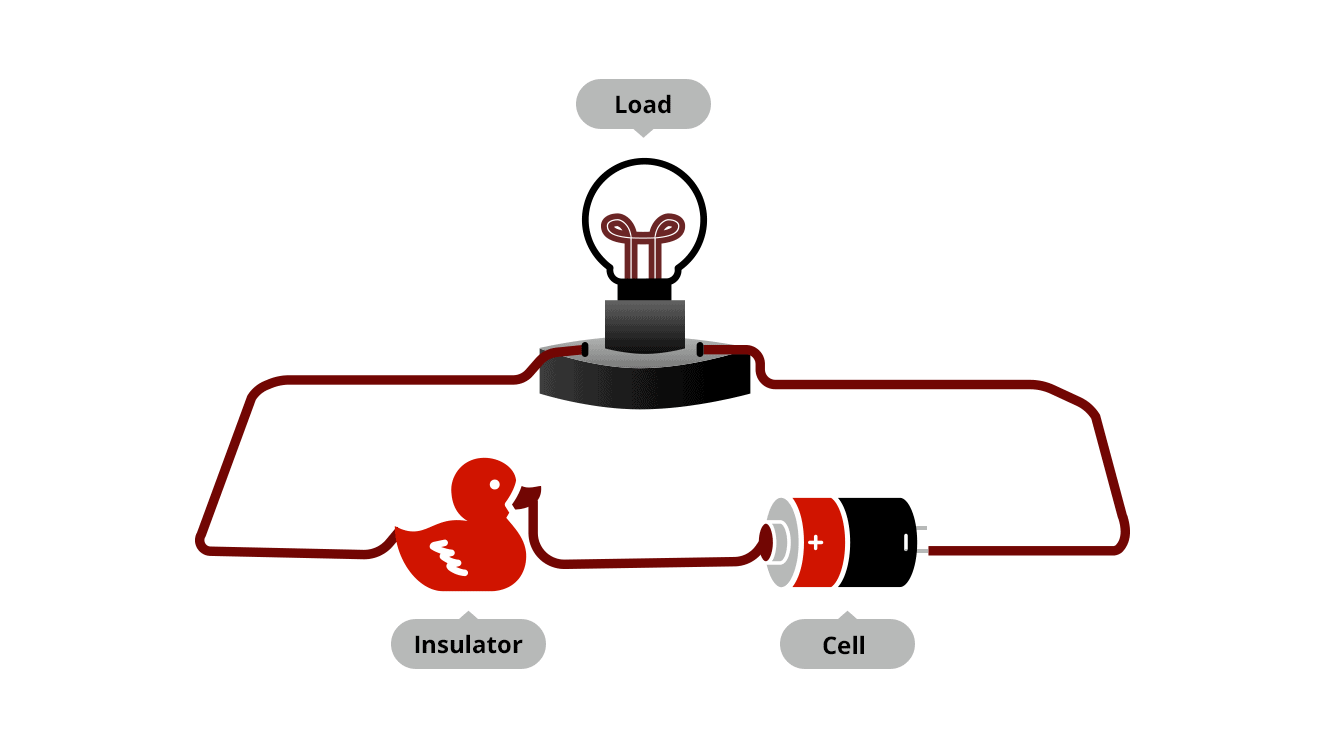
3. A Glimpse at the Process
The following illustration points out the process of electrical insulation:
4. Applications That Use Electrical Insulation
Some of the primary applications that require electrical insulation include:
- Automotive components
- Computers and computer peripherals
- Consumer products
- Conventional and uninterruptible power supplies
- Electrical and power distribution systems
- Lighting
- Medical equipment
- Telecommunications equipment
5. Commonly Used Electrical Insulation Materials
There are many types of electrical insulation materials available. Some of the most commonly used include:
- Cardboard/Paper: These materials are a cost-effective option for insulation applications involving low heat and voltages.
- Clay (ceramic or porcelain): This material is the standard for high-voltage and radio-frequency (RF) insulators.
- Glass (limestone, silica, and soda ash): This material is used occasionally in low-voltage applications.
- Mica: This material offers good electrical insulation and thermal conduction properties.
- Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA): This material is flexible, transparent, and chemical resistant. It is commonly used in near-ocean applications due to its salt spray resistance.
- Rubber: This material was used as an insulation in natural and synthetic variations up until the 1950s. However, it has since been largely replaced with plastics.
The experts at ESPE Manufacturing fabricate a variety of custom parts and products from electrical insulation material. Check out the list below to see the material options available.

Electrical Insulation Material Offerings and Options at ESPE
At ESPE, we utilize a wide range of electrical insulating materials in our custom manufacturing operations. The primary materials we work with are:
- Formex: Formex is a brand of electrical insulation materials, all of which are made from flame-retardant polypropylene. They are a versatile and cost-effective solution for a variety of applications, ranging from consumer appliances and electronics to commercial data centers to industrial-scale systems.
- Nomex: Nomex is a line of paper and pressboard insulation products. These meta-aramid polymer materials offer chemical, thermal, and radiation resistance in addition to their electrical insulation properties. They are commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, power generation, and marine industries.
- Fishpaper/Vulcanized Fibre: Fishpaper is the generic term for electrical grade vulcanized fibre. It is lightweight, easy to work, and resistant to hot and cold conditions. It is often used in the production of components such as bushings, washers, gaskets, and more. Fibre is the generic term for commercial grade vulcanized fibre. It is hard, durable, and chemically pure and offers excellent strength, flexibility, and workability. It is often used in the manufacture of components such as gaskets, insulating plates, and washers.
We also offer a variety of other types and grades of electrical insulating plastics and papers.
ESPE Manufacturing: Your Expert and Partner for Electrical Insulation
Electrical insulation is essential to ensuring electrical and electronic devices, equipment, and systems are safe. However, the type employed depends on the application, with different applications requiring different electrical resistivity and other physical, mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties. While determining which electrical insulating materials are right for your application can be difficult, the experts at ESPE Manufacturing are here to help.
Whether you’re looking for an electrical insulation material supplier or a manufacturer of electrical insulating parts and products, we can meet your needs. To learn more about our material offerings and options, check out our material catalog. To discuss your material or manufacturing needs with one of our experts, contact us or request a quote today.
Stamped Parts for Electrical Insulation
Leave a CommentAt ESPE Manufacturing Co., we provide high-quality electrical insulation materials and fabricated plastic parts. In addition to stocking and distributing a large inventory of non-metallic materials, we offer custom fabrication capabilities ranging from prototype to full production runs.
Stamping is one of our fabrication specialties. We produce a wide range of stamped products made from electrical insulation and barrier materials—including ITW Formex®, ITW Statex®, and Nomex®—as well as from other non-metallic materials such as plastics and aramid papers.
Stamping Process for Non-Metal and Plastic Parts
Stamping is a manufacturing technique that involves using a custom-designed punch and die block set to punch out parts from the workpiece. The stock material—typically in strip or coil form—sits in-between the punch and the die block. Once the material is in position, the punch forces through it into the die block, stamping out the part.
ESPE’s stamping operations include slitting the material down, then feeding it into the presses where the stamping takes place at 50-200 strokes per minute. In a single press stroke we can produce up to 5 blanked parts.
When selecting a plastic or other non-metal material for a stamping operation, it is important to keep in mind a few factors to ensure optimal part performance and production. These considerations include the material’s:
- Mechanical, electrical, magnetic, and thermal properties
- Performance characteristics, including durability and performance under normal and high-stress operating conditions
Careful consideration should also be taken for other design elements, including ensuring the design fulfills the absorption, compression, and alignment requirements of the application.
A wide range of insulation materials are used in non-metal stamping operations, including:
- ITW Formex® and ITW Statex®. These materials are suitable for applications with a high electrostatic discharge (ESD) profile. They are effective barriers to static electricity since they prevent its build-up and dissipate it. They are a good choice for parts used in computers, consumer electronic devices, medical equipment, solar energy components, and telecom appliances.
- Nomex® paper. This material is used in flat-panel TVs, tablets, and mobile phones due to its excellent electrical and thermal insulation properties.
- Fishpaper/vulcanized fiber. This material is lightweight and performs well in environments with alternating high and low temperatures. Some of the items commonly made using fishpaper include circuit breakers, gaskets, and bushings for motors.
Two Advantages of Plastic Stamping for Electrical Barriers and Insulators
There are a couple of advantages to using stamping for manufacturing non-metallic parts and products, such as electrical barriers and insulators. These advantages include:
- Higher accuracy and tighter tolerances. Depending on the state of the die, the stamping process can produce high volumes of identical parts with very strict tolerances.
- Greater reusability and flexibility. Although the initial process of producing a custom die set is time-consuming, once a die is ready, it can be used for multiple production runs or swapped out quickly for different parts. At ESPE, these process qualities allow us to offer our customers a typical lead time of 5–15 days with emergency and rush options on a case-by-case basis.
Applications of Stamped Electrical Barriers and Insulators
Due to its numerous advantages, stamping finds application in a wide range of industries. Industries that utilize stamped electrical barriers and insulators include:
- Aerospace
- Agriculture
- Architecture
- Automotive
- Defense and military
- Dental and medical
- Electronics
- Food and beverage
- Machine tools
- Marine
- Oil and gas
- Packaging
- Renewable energy
Stamped Insulation Solutions From ESPE Manufacturing
Stamping is a quick and cost-effective method of manufacturing high volumes of high-quality non-metallic parts, including electrical barriers and insulators.
As an industry-leading supplier of electrical insulation and barrier materials, ESPE has the knowledge and experience to fabricate custom parts from these substrates. Our stamping capabilities allow us to form parts from these and other non-metallic substrates.
To learn more about our stamping capabilities or to partner with us on your next project, contact us or request a quote today. We typically respond to quote requests in 24 hours or less.
